Teacher information:
The Problem
Design and build a bridge out of 4 mm square balsa wood, glue, string and paper that will span a 500mm gap and will hold a two kilogram weight suspended from under or on top of the centre of the span. The bridge has a construction budget which cannot be exceeded, each piece of material has a specific cost per unit.
This project is a primer to the other projects in this section. The knowledge gained in structural design in this problem will be transferable to the other projects. The Brick Powered Vehicle, the Rat Trap and the Arm can all incorporate the ideas learned from the Hold Up for light, strong chassis and and other structural parts.
The students should be encouraged to look around them and notice the design of bridges, roof supports, table braces etc. The discovery and discussion of the various methods of structural supports should take one or two class room sessions. Some of the areas to cover would be;
a) Tension forces.
b) Compression forces.
c) Loading forces. ..................... concentrated, uniformly distributed
d) Shear forces.
Types of Beams:
a) Simple beam.......supported at each end.
b) Cantilever............fixed at one end.
c) Continuous...........supported at more than two points.
d) Fixed...................... both ends solidly planted.
Notes on Beam design:
The ability of a beam to resist bending depends on the material used, the shape of the cross section and the way the cross section is turned in respect to the load. Demonstrate this to the class by bending a wood or steel ruler across its thin axis. It bends easily. Now turn the ruler and bend it across its wide axis, can't be done. It is nearly impossible to bend the ruler in the direction of its width. Thus what should be pointed out is that the resistance to bending of a beam is related to its cross section. (the technical term is "section modulus")
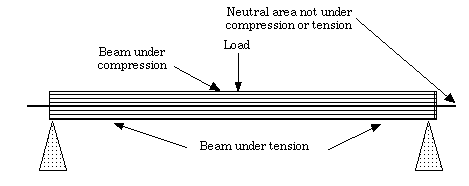
Example of a Beam under Load
This sample of a beam under load shows where the forces are. This may be used to help students understand how to design a structure for strength.

Each piece of balsa wood that is used can be considered a simple square beam. These will follow the example of the above beam when under load. If several pieces of balsa are glued together to form a truss the strength of the assembly increases a great deal.
In a truss shape; as shown below, the triangle is the main form. The triangle is the strongest shape because the load is spread equally across all components leaving no one part taking a greater load than the others
Truss Terminology
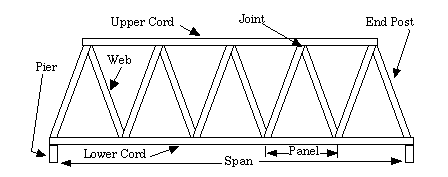
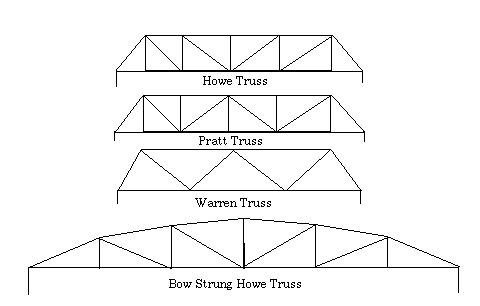
Below are several examples of various simple trusses that the students can use in the development of their project. Any book that discusses industrial building or engineering will be a good source for information that can be used in instructing the students.
When the students are designing their bridge they must be aware that all the load placed on the bridge will have to go to ground at each end. There should be special consideration to the piers at each end and how they will carry the load. Often students overlook this and the bridge fails at the piers first, well before the main span will fail. Small paper gussets can be used to give added strength at web joints, piers etc.
The Materials
• 1/8 x 1/8 (4mm) balsa wood • Lepages fast drying model wood glue
• Butchers string • Straight pins, 100 per bridge
• Card stock • Wax paper
• Roll of white drawing paper • Exacto knives/hobby blades
• Card board for pinning drawing to, old boxes etc, but must be flat!
* If you have availability to the Video "Bridges" it should be shown as an introduction to the project. Then use the worksheet provided in this section for the students to work on.
The Process
• The basic method of brianstorming and using the journals should be followed.
• In teams of two, one person will design the bridge sides and the other the bridge deck. Only one side needs to be drawn!
• Full scale detailed drawings of the side and top elevations of the bridge are done first. These will be the pattern for cutting out the balsa wood components. Mark before butting starts.
• Tape drawings to card board back. One team member will do the sides and the other the deck and any other components as needed.
• Tape the wax paper to the drawings.
• The students will "purchase" materials as needed. Record this in a copy of their purchase sheet that the teacher will have. These purchases must also be recorded by the student in their record book.
Reselling of materials to other students is not allowed.
• Layout and measure the balsa wood to fit the drawing. Cut the material on a cutting board (piece of card board) and pin it in place on the drawing glueing as needed.
• When all components are finished, assemble the sides and deck and any cross braces etc that are needed.
Joints:
Good joint, flush cut. Poor joint, little wood to wood contact
glue by itself is not strong!
Accuracy:
Make sure that the card board is flat and that there is no twist to the components and that both sides are exactly the same.
Pins:
Pins must be placed beside the wood not through it. Putting pins through the wood makes for a weak bridge. Also make sure pins are not used in the joints as a strengthening component.
Design Outline
Design and build a bridge out of 4 mm square balsa wood, glue, string and paper that will span a 500mm gap and will hold a two kilogram weight suspended from under or on top of the centre of the span. The bridge has a construction budget which cannot be exceeded, each piece of material has a specific cost per unit. The bridge also has specific dimensions to which the contractor must adhere.
Design Criteria Material Cost
Construction Hints:
*teacher set costs per item and total cost i.e. bridge = 12,456,000*
a) The triangle is the strongest of shapes.
d) I beams are stronger that square bars.
c) Light and strong is better than thick and heavy.
d) A piece of paper under tension is stronger than under compression.
e) Trusses are made up of triangles.
Marking: Total marks inc. student performance = 200
A) Size:-----value 20 lose one mark for every 2 mm oversize in each direction measured at four positions.
B) Strength:---- value 20 lose one mark for every 100 grams under spec.. load; gain one mark for every 100 gr. over spec..
C) Cost: ----value 20 lose one mark for every 1000 dollars over cost; gain one mark for every 1000 dollars under cost.
D) Deflection:-----value 20 lose one mark for every 2 mm deflection past one centimetre; gain one mark for every 2 mm less than one centimetre.
E) Construction: -------value 20 Teacher's Evaluation of your project.
Student Lab
Design and build a bridge out of 4 mm square balsa wood, glue, string and paper that will span a 500mm gap and will hold a two kilogram weight suspended from under or on top of the centre of the span. The bridge has a construction budget which cannot be exceeded, each piece of material has a specific cost per unit.
The Materials
• 1/8 x 1/8 (4mm) balsa wood • Lepages fast drying model wood glue
• Butchers string • Straight pins, 100 per bridge
• Card stock • Wax paper
• Roll of white drawing paper • Exacto knives/hobby blades
• Card board for pinning drawing to, old boxes etc, but must be flat!
The Process
• The basic method of brianstorming and using the journals should be followed.
• In teams of two, one person will design the bridge sides and the other the bridge deck. Only one side needs to be drawn!
• Full scale detailed drawings of the side and top elevations of the bridge are done first. These will be the pattern for cutting out the balsa wood components. Mark before butting starts.
• Tape drawings to card board back. One team member will do the sides and the other the deck and any other components as needed.
• Tape the wax paper to the drawings.
• The students will "purchase" materials as needed. Record this in a copy of their purchase sheet that the teacher will have. These purchases must also be recorded by the student in their record book.
Reselling of materials to other students is not allowed.
• Layout and measure the balsa wood to fit the drawing. Cut the material on a cutting board (piece of card board) and pin it in place on the drawing glueing as needed.
• When all components are finished, assemble the sides and deck and any cross braces etc that are needed.
Joints:
Good joint, flush cut. Poor joint, little wood to wood contact glue by itself is not strong!
Accuracy:
Make sure that the card board is flat and that there is no twist to the components and that both sides are exactly the same.
Pins:
Pins must be placed beside the wood not through it. Putting pins through the wood makes for a weak bridge. Also make sure pins are not used in the joints as a strengthening component.
Design Outline
Design and build a bridge out of 4 mm square balsa wood, glue, string and paper that will span a 500mm gap and will hold a two kilogram weight suspended from under or on top of the centre of the span. The bridge has a construction budget which cannot be exceeded, each piece of material has a specific cost per unit. The bridge also has specific dimensions to which the contractor must adhere.
Design Criteria Material Cost
1) Length = 60 cm. 1) Wood = $ _____ per. centimetre *
2) Width = 10 cm. 2) Glue = $ ______ per. drop *
3) Height = 14 cm. 3) String = $______ per. centimetre *
4) Cost = $ ___________ * 4) Paper = $ ______ per. square cm. *
Construction Hints:
*teacher set costs per item and total cost i.e. bridge = 12,456,000*
a) The triangle is the strongest of shapes.
d) I beams are stronger that square bars.
c) Light and strong is better than thick and heavy.
d) A piece of paper under tension is stronger than under compression.
e) Trusses are made up of triangles.
Marking: Total marks inc. student performance = 200
A) Size:-----value 20 lose one mark for every 2 mm oversize in each direction measured at four positions.
B) Strength:---- value 20 lose one mark for every 100 grams under spec.. load; gain one mark for every 100 gr. over spec..
C) Cost: ----value 20 lose one mark for every 1000 dollars over cost; gain one mark for every 1000 dollars under cost.
D) Deflection:-----value 20 lose one mark for every 2 mm deflection past one centimetre; gain one mark for every 2 mm less than one centimetre.
E) Construction: -------value 20 Teacher's Evaluation of your project.
_____/20
Name:
___________________
Partner: __________________
Block #
_________
Part A
1. The three kinds of bridges:
1. _______________________ 2 _____________________ 3_____________________
2. A _______________ bridge rest on supports at each end.
3. A truss bridge is a _______________ bridge with one or more ________________
4. Supports called ______________ make them longer.
5. ____________ braced with trusses are called ________________ bridges.
6. A cantilever bridge is a variation of a _________________ bridge.
7. An _______ bridge is very strong and can carry heavy loads.
8. The stone at the top is called the ________ stone.
9. The ___________________ bridge is held together by very strong cables stretched over tall towers.
10. _____________ attache the cable to the deck.
11. __________________ bridges are used to span deep or wide obstacles.
12. Steel ________________ placed on both side of the deck stop it from sagging.
13. A ________________ bridge floats on the water.
14. When crossing rivers,a _________________ is sunk to the bottom of a river as a support for the bridge ____________.
PartB:
List the bridges which you could find within a 10 minute drive of the city.
State the location of the bridge and its type of construction.
Location Construction
1 __________________________________________________________________________
2 __________________________________________________________________________
3 __________________________________________________________________________
4 __________________________________________________________________________
5 __________________________________________________________________________
6 __________________________________________________________________________
7 __________________________________________________________________________
8 __________________________________________________________________________
9 __________________________________________________________________________
10 __________________________________________________________________________
|
|